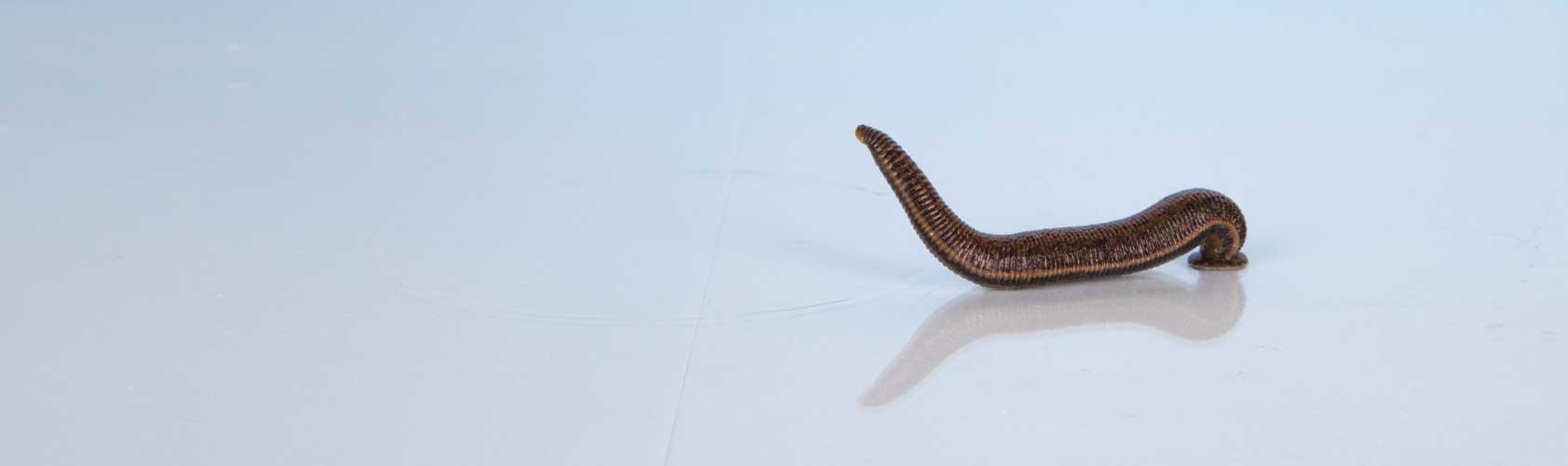

The Earth is home to over 600 species of leech. At 450 million years of age, they have a long history of evolution behind them and are therefore significantly older than dinosaurs, for example. Leeches have survived because they have evolved very differently to adapt to their respective habitats. The first species did not feed on the blood of vertebrates, as vertebrates and indeed mammals first appeared millions of years later. The external appearance of medicinal leeches is fascinatingly diverse. Some species have very light, yellowish skin with subtle dorsal markings; others are more of a medium to dark green, often with pronounced orange patterns and two light "rally stripes" on the sides, and still others have nearly black backs.
Their abdominal markings are also different. Some species are an even light olive green, while others have distinctive dark spots or are almost black. Zoologically speaking, they are different species.
The three species Hirudo medicinalis, Hirudo orientalis and Hirudo verbana were originally treated as colour variations of the same species and grouped under the term “medicinal leech” (“Hirudo medicinalis”). These days, medicinal leeches can be clearly differentiated into these three distinct species on the basis of molecular biological data. They can also be differentiated by their colour patterns. Leeches are protandrous hermaphrodites. Each leech has both male and female reproductive organs. Two leeches are involved in the mating process, during which each leech fertilises the other. From a few weeks up to a year after fertilisation, each leech lays 3 to 5 cocoons in moist soil. Each cocoon contains 5 to 25 eggs. After a development period of 5 to 9 days, all organs in the embryo are fully matured and the larvae begin to feed on the albumin in the cocoon. They complete their metamorphosis inside the cocoon. After approximately 30 days, the young hatch from the cocoon. They become sexually mature after around 3 years, and can live for more than 20 years.
All species of the Hirudo genus are ectoparasites and feed on blood. In the first phase of life, the juveniles mainly use amphibians as a food source, while the adults mainly parasitise birds and mammals. To locate hosts, leeches use photoreceptors, heat receptors and chemoreceptors located on their front suckers. If a leech perceives movement or vibrations in the water or changing light conditions in its environment, it swims towards the potential food source. If the leech is already in the vicinity of a potential host, it perceives the host’s body heat.
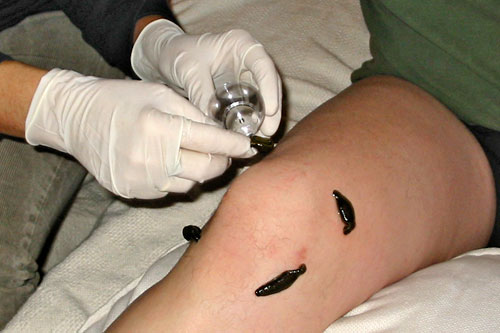
Leech bites are rarely painful. This makes sense, as leeches in the wild have no interest in being noticed by their host food sources. Leeches have three star-shaped jaws, each with around 80 calcareous teeth, which they use to carefully cut through the skin to get to the blood, their source of food. Between the leech’s teeth are openings through which its saliva is released. Leech saliva contains a variety of substances.
